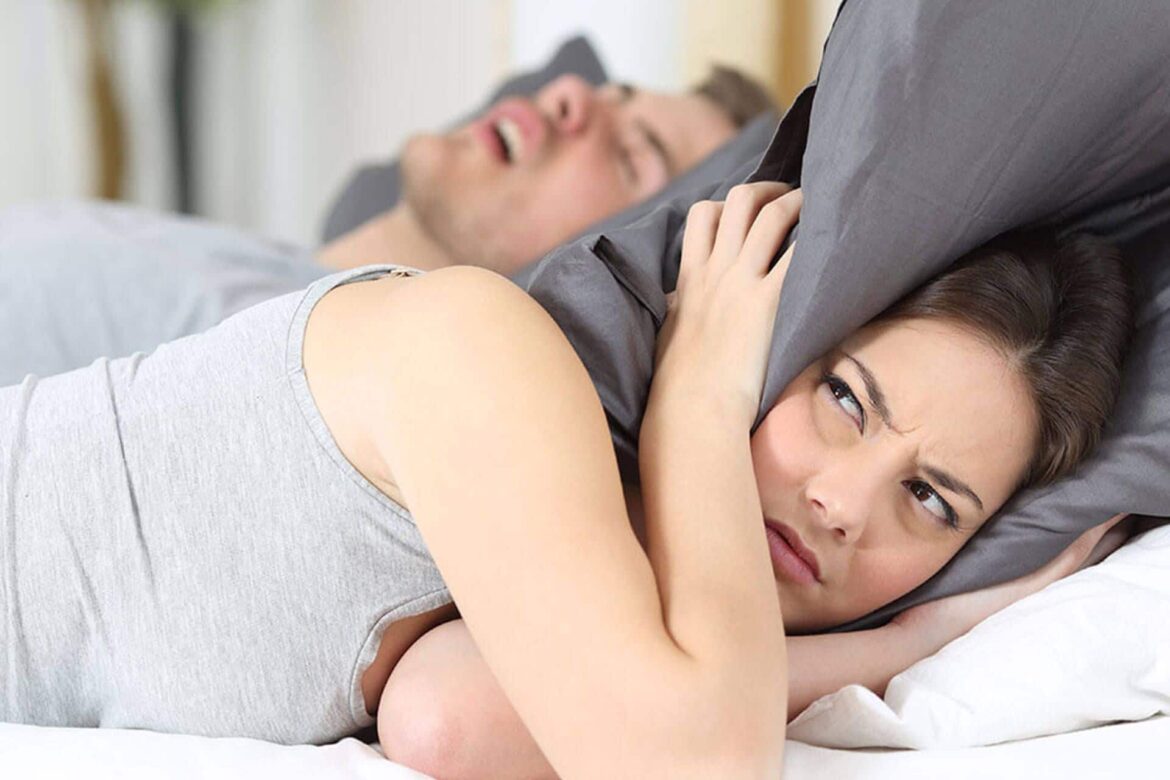
Sleep apnea, particularly Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), isn’t just a solo struggle; it’s a duo dilemma when you share your bed. The wheezing, snoring, and sudden silences followed by gasps can disrupt the night’s peace—not just for the one with OSA but for the sleep partner as well.
However, with understanding and strategic management, you can prevent this medical condition from driving a wedge between you and your partner. This comprehensive guide explores how couples can navigate the choppy waters of OSA without sinking their romantic relationship.
OSA is caused by a blockage of the airway while CSA occurs when your brain fails to send the right signals to the muscles responsible for controlling breathing. Here’s a comprehensive guide to snoring problems: https://drsomaent.com/obstructing-sleep-apnea-singapore-a-comprehensive-guide-to-snoring-problems/.
Sleeping Together with OSA ─ How Not to Kill Your Love Life
Source: opmed.doximity.com
Sleep apnea, particularly Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), isn’t just a solo struggle; it’s a duo dilemma when you share your bed. The wheezing, snoring, and sudden silences followed by gasps can disrupt the night’s peace—not just for the one with OSA but for the sleep partner as well.
However, with understanding and strategic management, you can prevent this medical condition from driving a wedge between you and your partner. This comprehensive guide explores how couples can navigate the choppy waters of OSA without sinking their romantic relationship.
The Noisy Elephant in the Bedroom
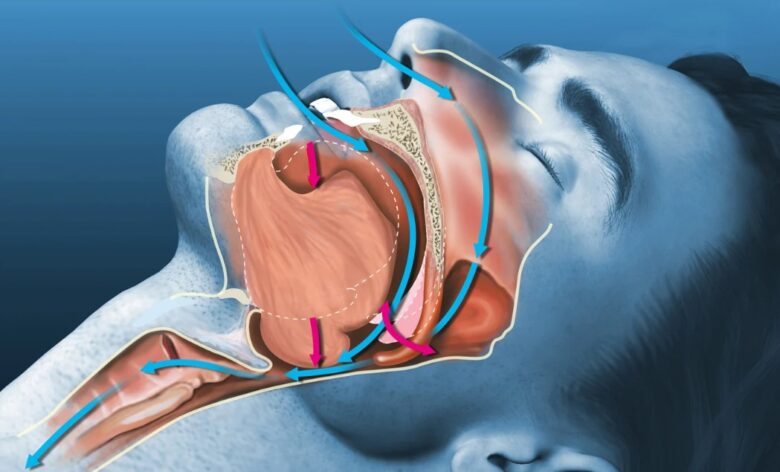
Obstructive Sleep Apnea is characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, caused by the blocking of the upper airway. These interruptions can occur multiple times per hour, and the resultant loud snoring and gasping for air can severely impact a partner’s sleep quality.
Beyond the noise, the person with OSA often experiences fragmented sleep, leading to daytime fatigue, irritability, and decreased libido—factors that can cool the warmest of connections.
Understanding the mechanics of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the first step in tackling its impacts. Typically, the throat muscles fail to keep the airway open, despite efforts to breathe. The condition is often associated with factors such as obesity, a narrow airway, or even genetics. The disruption to sleep patterns can lead to significant health issues like hypertension, heart disease, and diabetes, making it essential not just for the relationship’s sake, but for overall health to manage the condition effectively.
Communication is Key
When dealing with OSA, open communication can form part of the bedrock of your coping strategies. Both partners must express how the condition affects their sleep and daily life. A partner without OSA might feel reluctant to bring up their exhaustion for fear of seeming unsupportive, but keeping silent about their sleep deprivation can breed resentment and emotional distance.
The partner suffering from OSA, on the other hand, may feel vulnerable or embarrassed about their condition. They might withdraw from discussing how isolated or guilty they feel, which can be compounded by the lack of restorative sleep. Both partners should strive for empathy and support, acknowledging the problem without blame and focusing on solutions collaboratively.
Seeking Professional Help

Source: health.com
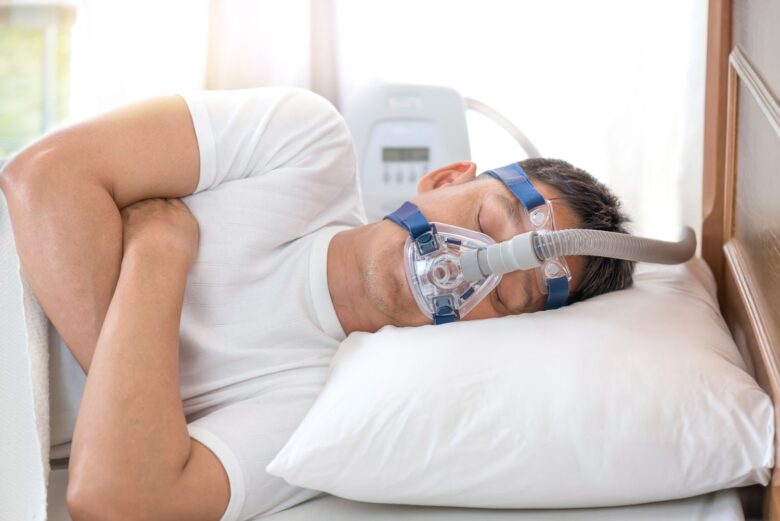
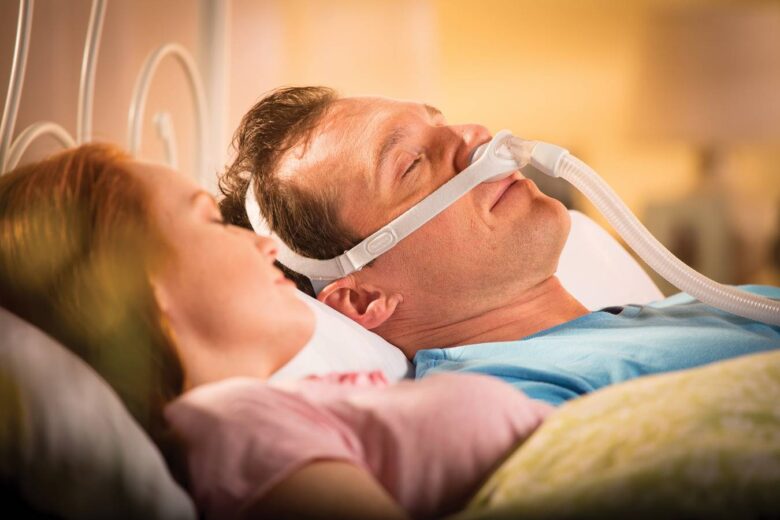
An important step in managing sleep apnea involves seeking help from healthcare professionals. This might include consultations with a sleep specialist who can recommend appropriate treatments such as CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) therapy, oral appliances, or even surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. Treatment not only improves health outcomes but also enhances the quality of life for both partners.
Couples should attend medical appointments together when possible. This not only shows solidarity but also helps the partner without OSA understand the complexity of the condition and the specifics of the treatment plan. It also provides an opportunity to discuss concerns or observations that might be helpful to the healthcare provider.
Redefining Sleep Hygiene
Revamping your sleep environment and habits, or sleep hygiene, can also mitigate some challenges of sleeping together with OSA. Consider maintaining a cool, quiet, and comfortable bedroom. Invest in a high-quality mattress and pillows that support proper alignment and comfort. While the CPAP machine might initially seem intrusive, its design has become more user-friendly and quiet, significantly lessening disturbances.
Adjusting bedtime routines can also play a crucial role. Limiting exposure to screens, dimming lights an hour before bedtime, and engaging in relaxing activities like reading or gentle yoga can help both partners wind down and sync their sleep schedules better.
If snoring is still a barrier, experimenting with different sleeping arrangements temporarily, such as using separate bedrooms or twin beds, can be considered. Remember, the goal is restful sleep for both, which is foundational to health and relationship well-being.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle plays a pivotal role in managing OSA. Weight loss, regular physical activity, and a healthy diet can reduce the severity of the symptoms. Alcohol, sedatives, and smoking are known aggravators of sleep apnea and should be avoided. Even changes like altering sleep positions can reduce symptoms; sleeping on one’s side instead of the back can prevent the tongue from blocking the throat.
Partners can support each other in these lifestyle changes by adopting healthier habits together. This could include preparing nutritious meals, exercising together, or even taking up new hobbies that encourage more active lifestyles. Such joint efforts not only improve health but also strengthen the relationship by building shared experiences and goals.
Navigating Emotional Currents
OSA can strain emotional bonds in a relationship. The partner without OSA might feel neglected or burdened, while the one with OSA might suffer from guilt and frustration over the disruptions caused. Acknowledging these emotions and addressing them through counseling or support groups can be beneficial.
Couples therapy can offer a safe space to explore these issues with the guidance of a professional who can help navigate the complex feelings and dynamics at play. Additionally, joining support groups where other couples share similar experiences can provide comfort and practical advice.
Conclusion
Living with Obstructive Sleep Apnea as a couple requires patience, understanding, and proactive management. It involves not just medical intervention, but also lifestyle and emotional adjustments.
By fostering open communication, seeking appropriate treatment, optimizing sleep environments, making lifestyle changes, and handling emotional challenges together, couples can maintain a strong, loving relationship despite the presence of OSA.
The key is to remember that you’re in this together—not just battling sleep apnea, but building a healthier future side by side.

